Let's Know CBG
Biogas:
Biogas is an energy-rich gas produced by anaerobic decomposition or thermochemical conversion of biomass. Biogas is composed mostly of methane (CH4), the same compound in natural gas, and carbon dioxide (CO2). The methane content of raw (untreated) biogas may vary from 40%–60%, with CO2 making up most of the remainder along with small amounts of water vapor and other gases. Biogas can be burned directly as a fuel or treated to remove the CO2 and other gases for use just like natural gas. Treated biogas may be called renewable natural gas or biomethane.manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste or food waste
Purification:
Production of biogas could be a continuous process. The utilization of biogas as an efficient energy source depends strongly on its methane concentration. Therefore, biogas purification is essential in order to have more energy per unit volume of compressed biogas and to get rid of the corrosive effect of H2S. This can be done by compressing the gas into the cylinders, which is possible only after removing carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and water vapour. Biogas purification increases the concentration of methane in biogas, in order to have fuel of higher calorific value. This can be achieved by decreasing the concentration of carbon dioxide. Elimination of carbon dioxide from the biogas helps to increase its calorific value as well as to eliminate the greenhouse gas.
Compression
It is possible to compress raw biogas, a mixture of CO2 and methane, between 150-250 bar, and transport it in composite gas cylinders (cascades).
Compressed Biogas (CBG)
CBG can be produced from waste, including municipal solid waste, sludge from wastewater treatment plants, market residues, agricultural residues, cattle dung, sugarcane press mud, sago waste, etc. The Union government had launched the Sustainable Alternative to Affordable Transport (SATAT) in October 2018 to promote the technology. The scheme targeted production of 15 million metric tonnes (MMT) of CBG by 2023. Public sector undertakings oil marketing companies (OMCs),IndianOil, BPCL, HPCL , GAIL and IGL have partnered with potential entrepreneurs under this initiative to set up plants and supply CBG to them for sale as automotive and industrial fuels.
The Future of CBG
The future of Compressed Biogas (CBG) is incredibly promising, as it represents a pivotal shift towards sustainable energy solutions. With increasing global focus on reducing carbon emissions, CBG stands out as a key player in the transition to a circular economy. This renewable energy source not only addresses waste management challenges but also offers a clean, low-carbon alternative to fossil fuels.
Looking Ahead:
As the world continues to seek out clean energy alternatives, CBG is poised to become a cornerstone of the global energy mix. Its potential to decarbonize sectors like transportation, agriculture, and industry makes it a crucial component of future energy strategies. At Panaceu, we are committed to leading this transformation, helping our clients and partners harness the full potential of CBG for a greener, more sustainable future.
CBG Production Flow Diagram
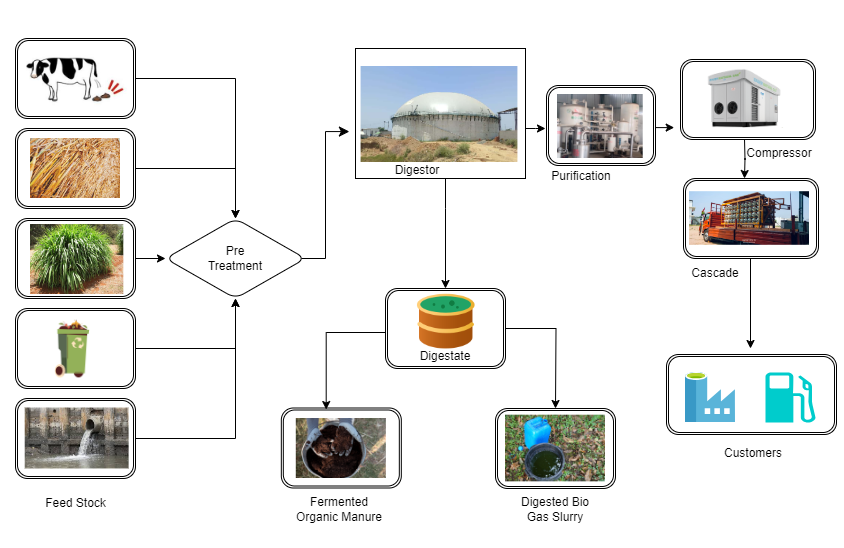
The only way to make this happened is to take action!
We believe in the power of collective action and invite you to join us in driving positive change. Together, we can create a more sustainable and equitable future by embracing innovative solutions and responsible practices. Be a part of the movement to make a lasting impact on our world—because every step toward change counts.